# A tibble: 409 × 4
percent_incr salary_type annual_salary performance_rating
<dbl> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
1 1 Salaried 1 High
2 1 Salaried 1 Successful
3 1 Salaried 1 High
4 1 Hourly 33987. Successful
5 NA Hourly 34798. High
6 NA Hourly 35360 <NA>
7 NA Hourly 37440 <NA>
8 0 Hourly 37814. <NA>
9 4 Hourly 41101. Top
10 1.2 Hourly 42328 <NA>
# ℹ 399 more rowsExam 1 Review
In 2020, employees of Blizzard Entertainment circulated a spreadsheet to anonymously share salaries and recent pay increases amidst rising tension in the video game industry over wage disparities and executive compensation. (Source: Blizzard Workers Share Salaries in Revolt Over Pay)
The name of the data frame used for this analysis is blizzard_salary and the relevant variables are:
percent_incr: Raise given in July 2020, as percent increase with values ranging from 1 (1% increase to 21.5 (21.5% increase)salary_type: Type of salary, with levelsHourlyandSalariedannual_salary: Annual salary, in USD, with values ranging from $50,939 to $216,856.performance_rating: Most recent review performance rating, with levelsPoor,Successful,High, andTop. ThePoorlevel is the lowest rating and theToplevel is the highest rating.
The top six rows of blizzard_salary are shown below:
Question 1
How rows observations are there in the blizzard_salary dataset and what does each row represent?
Question 2
Figure 1 (a) and Figure 1 (b) show the distributions of annual salaries of hourly and salaried workers. The two figures show the same data, with the facets organized across rows and across columns. Which of the two figures is better for comparing the median annual salaries of hourly and salaried workers. Explain your reasoning.


Question 3
Suppose your teammate wrote the following code as part of their analysis of the data.
They then printed out the results shown below. Unfortunately one of the number got erased from the printout, it’s indicated with _____ below.
# A tibble: 2 × 3
salary_type mean_annual_salary median_annual_salary
<chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Hourly 63003. 54246.
2 Salaried 90183. _____Which of the following is the best estimate for that erased value?
- 30,000
- 50,000
- 80,000
- 100,000
Question 4
Which distribution has a higher standard deviation?
- Hourly workers
- Salaried workers
- Roughly the same
Question 5
Which of the following alternate plots would also be useful for visualizing the distributions of annual salaries of hourly and salaried workers?
I. Box plot
II. Density plot
III. Pie chart
IV. Waffle chart- I
- I and II
- I, II, and III
- III and IV
Question 6
Next, you fit a model for predicting raises (percent_incr) from salaries (annual_salary). We’ll call this model raise_1_fit. A tidy output of the model is shown below.
# A tibble: 2 × 5
term estimate std.error statistic p.value
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 (Intercept) 1.87 0.432 4.33 0.0000194
2 annual_salary 0.0000155 0.00000452 3.43 0.000669 Which of the following is the best interpretation of the slope coefficient?
- For every additional $1,000 of annual salary, the model predicts the raise to be higher, on average, by 1.55%.
- For every additional $1,000 of annual salary, the raise goes up by 0.0155%.
- For every additional $1,000 of annual salary, the model predicts the raise to be higher, on average, by 0.0155%.
- For every additional $1,000 of annual salary, the model predicts the raise to be higher, on average, by 1.87%.
Question 7
You then fit a model for predicting raises (percent_incr) from salaries (annual_salary) and performance ratings (performance_rating). We’ll call this model raise_2_fit. Which of the following is definitely true based on the information you have so far?
- Intercept of
raise_2_fitis higher than intercept ofraise_1_fit. - RMSE of
raise_2_fitis higher than RMSE ofraise_1_fit. - Adjusted \(R^2\) of
raise_2_fitis higher than adjusted \(R^2\) ofraise_1_fit. - \(R^2\) of
raise_2_fitis higher \(R^2\) ofraise_1_fit.
Question 8
The tidy model output for the raise_2_fit model you fit is shown below.
# A tibble: 5 × 5
term estimate std.error statistic p.value
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 (Intercept) 3.55 0.508 6.99 1.99e-11
2 annual_salary 0.00000989 0.00000436 2.27 2.42e- 2
3 performance_ratingPoor -4.06 1.42 -2.86 4.58e- 3
4 performance_ratingSuccessful -2.40 0.397 -6.05 4.68e- 9
5 performance_ratingTop 2.99 0.715 4.18 3.92e- 5When your teammate sees this model output, they remark “The coefficient for performance_ratingSuccessful is negative, that’s weird. I guess it means that people who get successful performance ratings get lower raises.” How would you respond to your teammate?
Question 9
Ultimately, your teammate decides they don’t like the negative slope coefficients in the model output you created (not that there’s anything wrong with negative slope coefficients!), does something else, and comes up with the following model output.
# A tibble: 5 × 5
term estimate std.error statistic p.value
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 (Intercept) -0.511 1.47 -0.347 0.729
2 annual_salary 0.00000989 0.00000436 2.27 0.0242
3 performance_ratingSuccessful 1.66 1.42 1.17 0.242
4 performance_ratingHigh 4.06 1.42 2.86 0.00458
5 performance_ratingTop 7.05 1.53 4.60 0.00000644Unfortunately they didn’t write their code in a Quarto document, instead just wrote some code in the Console and then lost track of their work. They remember using the fct_relevel() function and doing something like the following:
What should they put in the blanks to get the same model output as above?
- “Poor”, “Successful”, “High”, “Top”
- “Successful”, “High”, “Top”
- “Top”, “High”, “Successful”, “Poor”
- Poor, Successful, High, Top
Question 10
Finally, your teammate creates the following two plots and ask you for help deciding which one to use in the final report for visualizing the relationship between performance rating and salary type. In 1-3 sentences, can you help them make a decision, justify your choice, and write the narrative that should go with the plot?
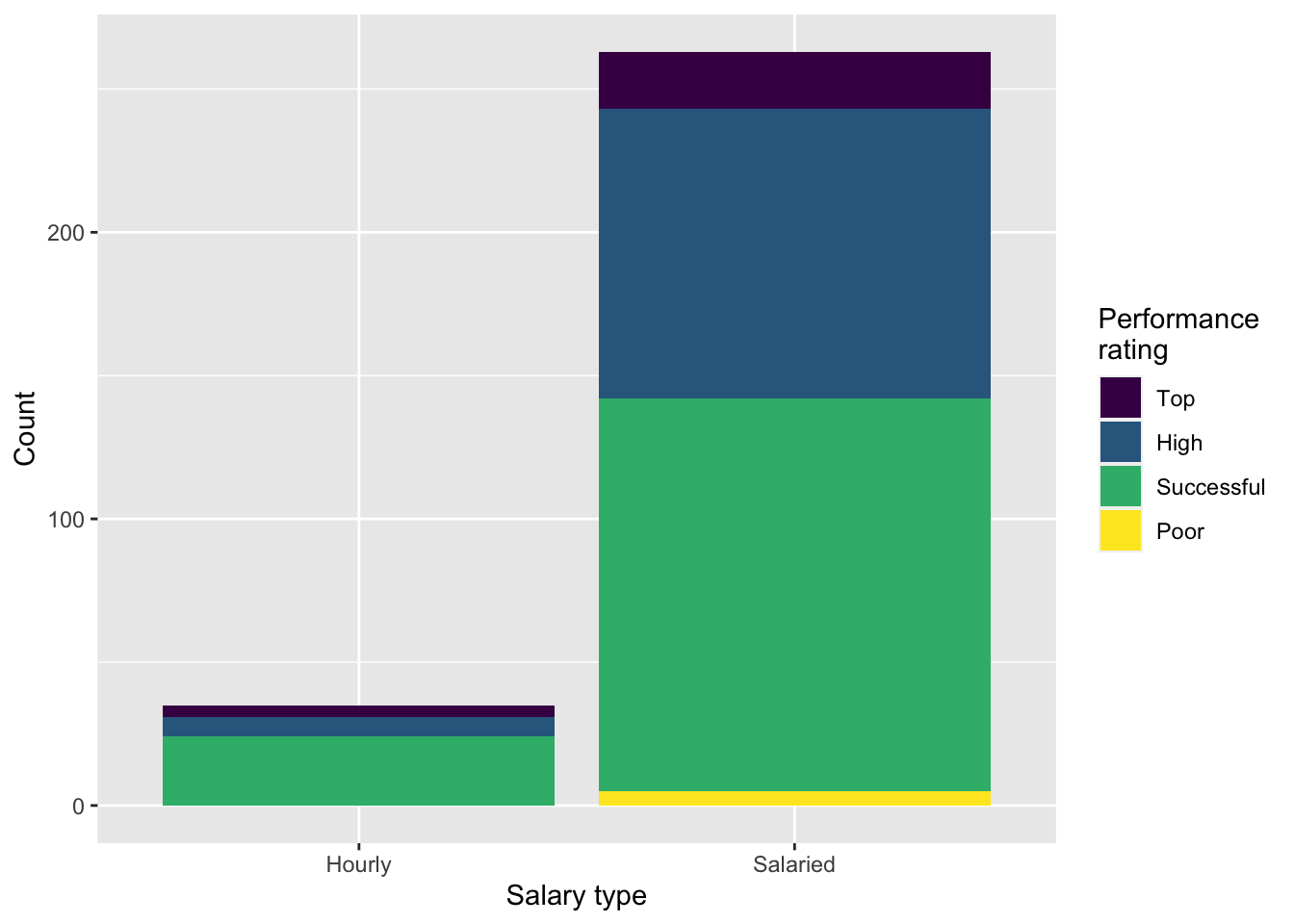
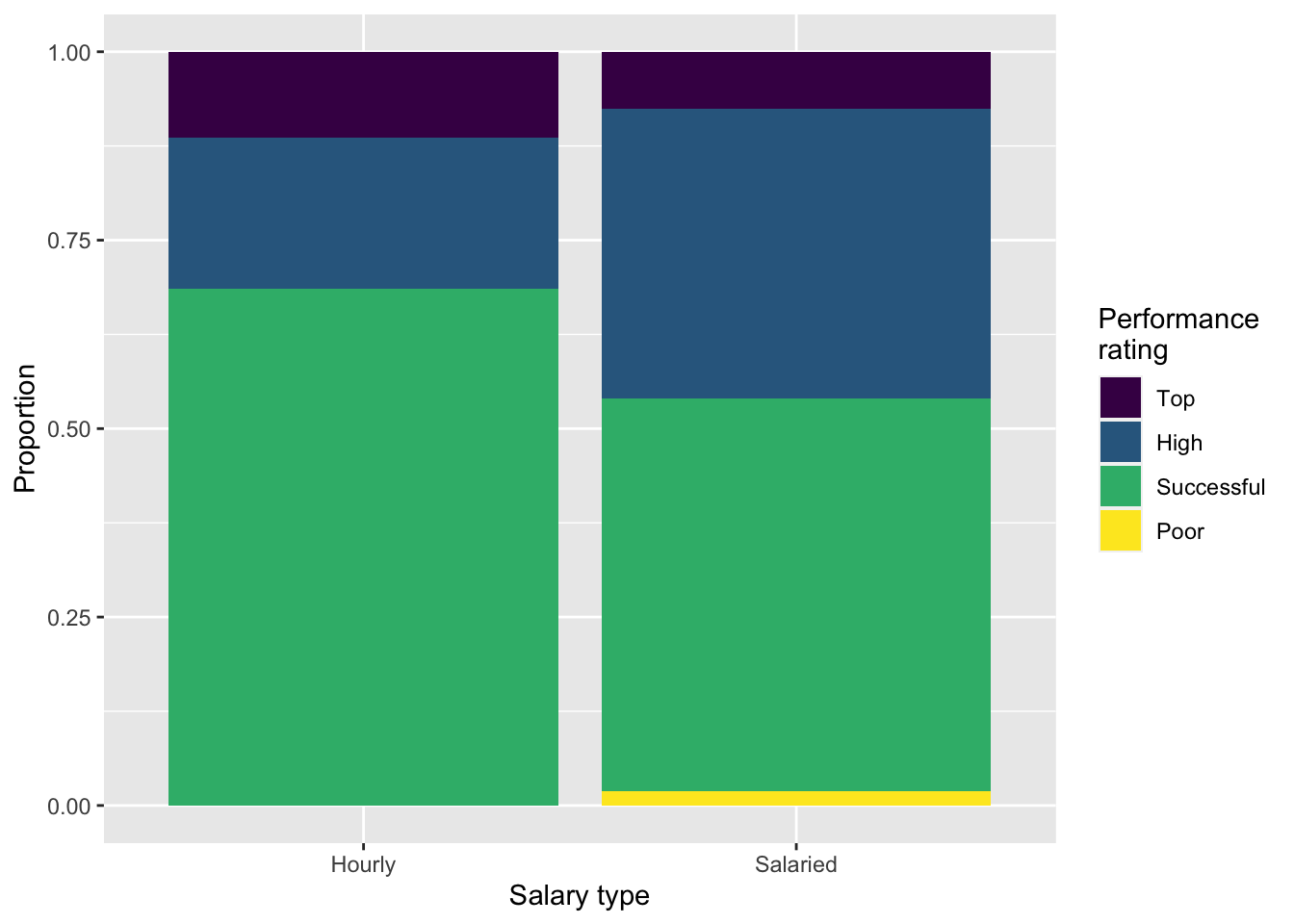
Question 11
A friend with a keen eye points out that the number of observations in Figure 2 (a) seems lower than the total number of observations in blizzard_salary. What might be going on here? Explain your reasoning.
Question 12
Show the proportions of performance ratings for hourly and salaried workers in a table and ask students to place those numbers on the segments of Figure 2 (b).
# A tibble: 4 × 3
performance_rating Hourly Salaried
<fct> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Successful 0.686 0.521
2 High 0.2 0.384
3 Top 0.114 0.0760
4 Poor 0 0.0190Question 13
Figure 3 is yet another visualization of the relationship between salary type and performance rating. What type of plot is ths, and what does it display that Figure 2 (b) doesn’t?

Question 14
Suppose we fit a model to predict percent_incr from annual_salary and salary_type. A tidy output of the model is shown below.
# A tibble: 3 × 5
term estimate std.error statistic p.value
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 (Intercept) 1.24 0.570 2.18 0.0300
2 annual_salary 0.0000137 0.00000464 2.96 0.00329
3 salary_typeSalaried 0.913 0.544 1.68 0.0938 Which of the following visualizations represent this model? Explain your reasoning.
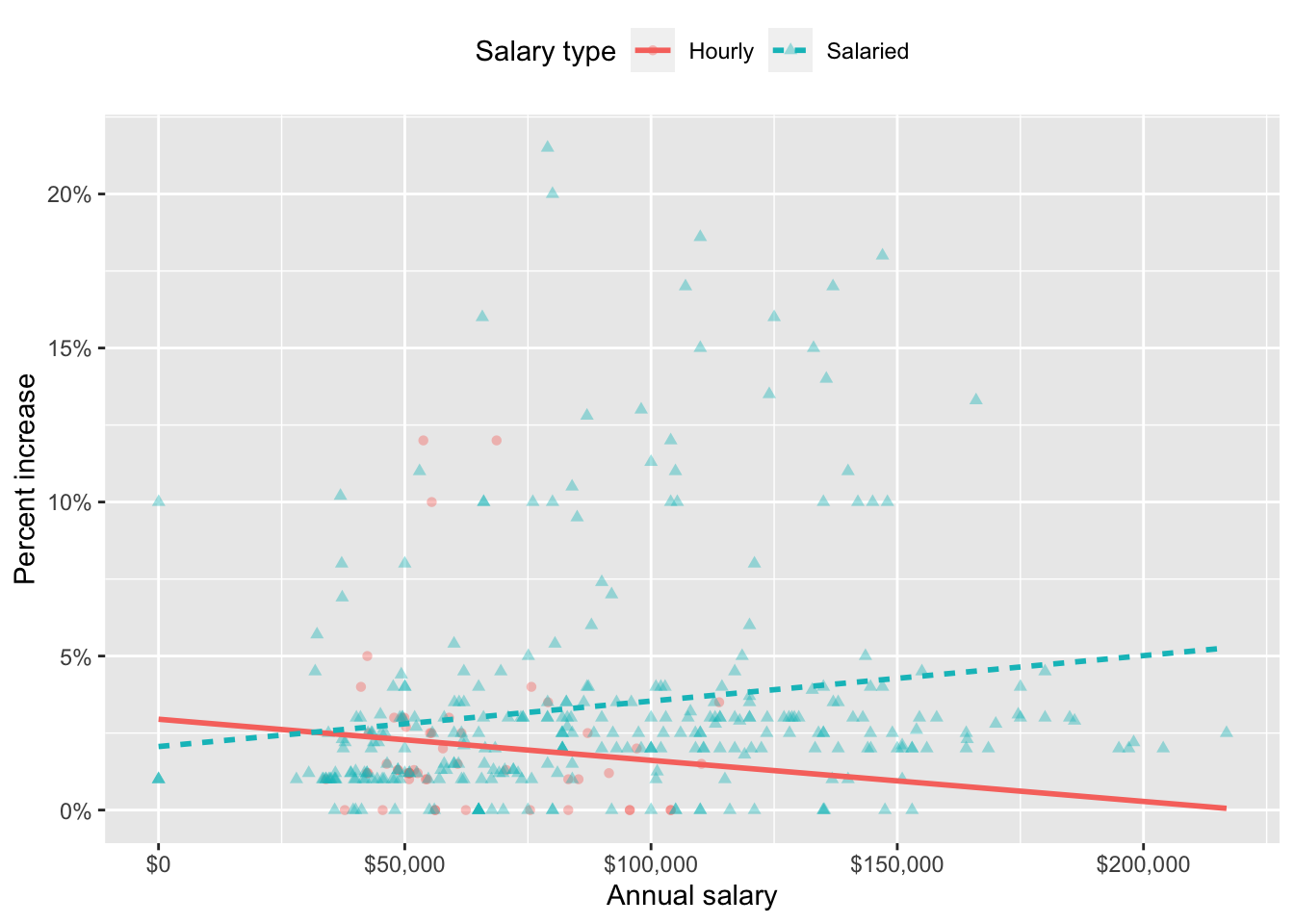
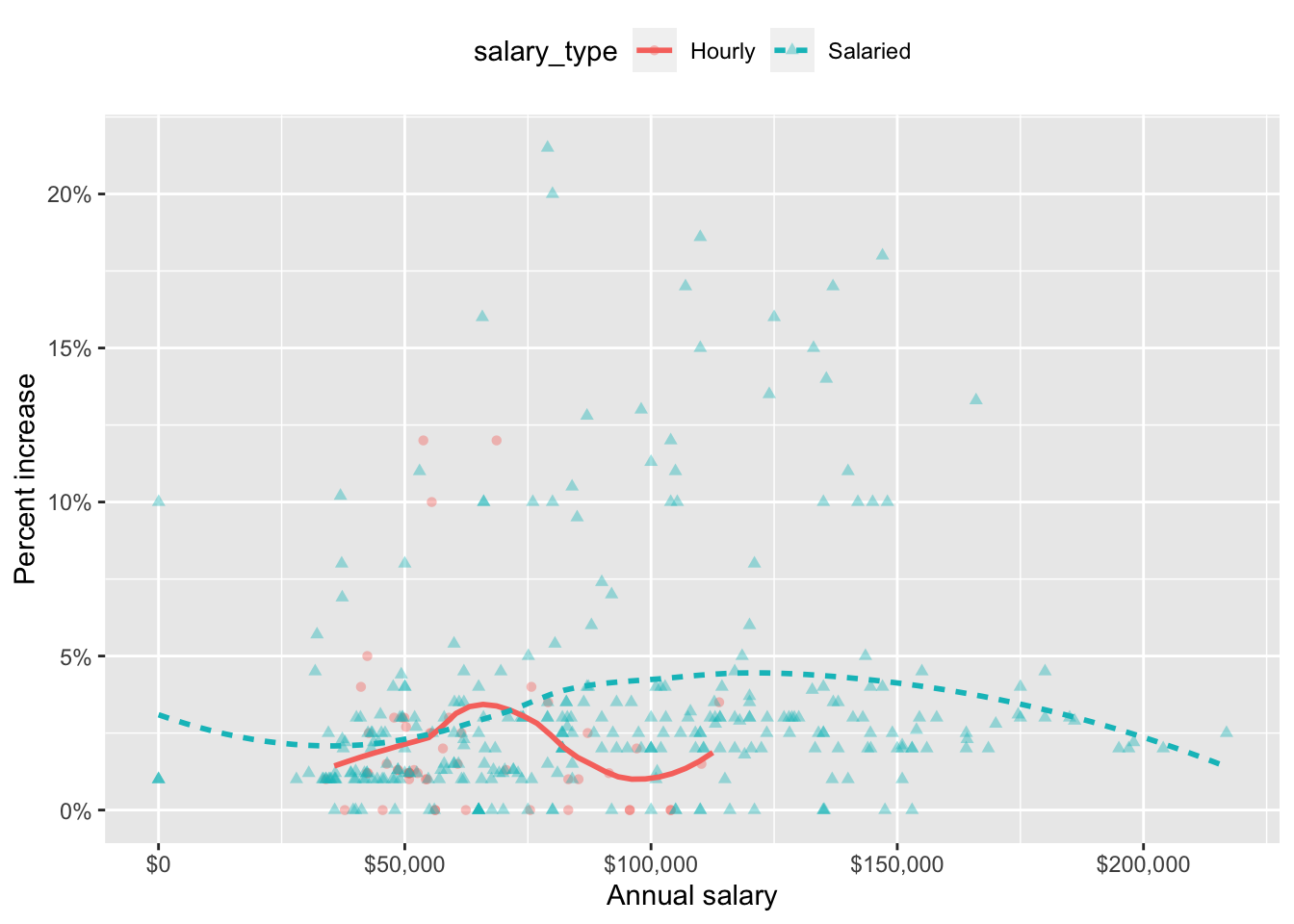
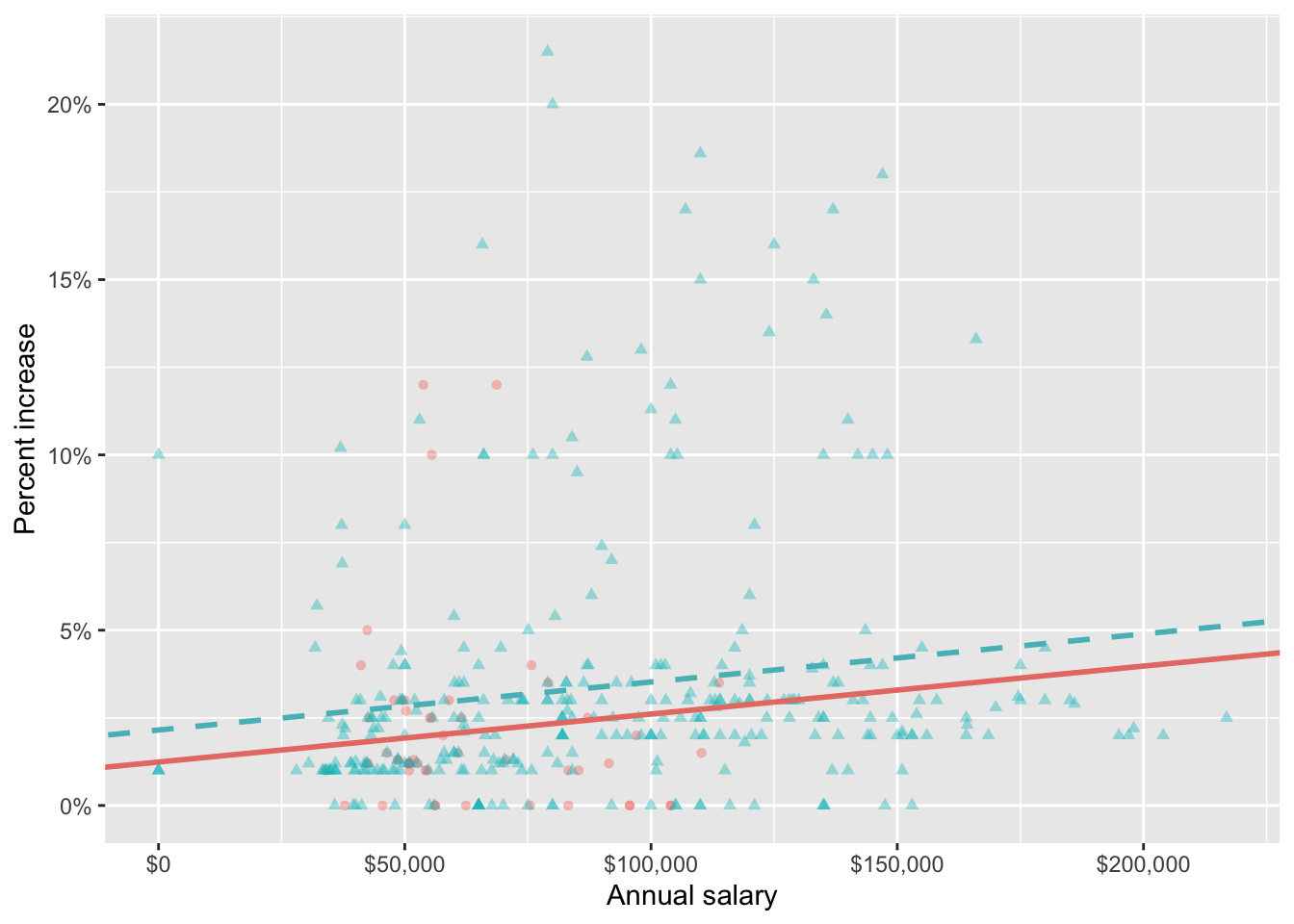

Question 15
Define the term parsimonious model.
Bonus
Pick a concept we introduced in class so far that you’ve been struggling with and explain it in your own words.
